Mastering SaaS sales in 2026 requires both strategic thinking and adaptable tactics. The subscription-based model has completely changed the software selling game, creating a whole new playbook for sales teams.
This guide will take you from the basics of SaaS sales through to advanced tactics that are proven to drive revenue growth. Along the way, we’ve packed it with practical steps to build killer sales processes, track the metrics that matter, and implement methodologies that deliver results.
You'll walk away with actionable strategies based on what's working right now in the industry. No fluff, just practical advice that you can apply immediately.
And speaking of practical tools, request a demo to discover how Leadfeeder can help you identify which companies visit your website, giving your sales team the intel they need to pursue qualified opportunities. Turn those anonymous website visitors into prospects and watch your conversion rates climb.
What is SaaS sales?
SaaS sales, or Software as a Service sales, involves selling software that's hosted in the cloud and delivered via subscription. Instead of a one-time purchase, customers pay recurring fees to access your software solution.
This subscription model transforms how sales teams operate, as you need to build ongoing relationships where value must be continuously demonstrated.
How is SaaS different from other types of sales?
Let’s dissect how the SaaS sales meaning differs from traditional alternatives:
There’s a recurring revenue focus: You're selling access, not ownership. This fundamental shift means building relationships that last years, not closing one-time deals.
Customer success directly impacts revenue: When customers can cancel anytime, their ongoing satisfaction determines your company's financial health.
Sales cycles tend to be shorter: Many SaaS products deploy quickly without extensive implementation—although this varies based on solution complexity.
Technical knowledge requirements run deeper: You need to effectively demonstrate value and address concerns about security, integration, and data management.
There are also three financial differences that shape the entire approach:
Traditional Sales |
SaaS Sales |
High upfront revenue |
Lower initial sale, higher lifetime value |
Focus on new customers |
Balance acquisition with retention |
Gross sales metrics |
Recurring revenue metrics (MRR, ARR) |
These differences create a ripple effect throughout the organization. SaaS sales teams collaborate more closely with marketing, product, and customer success than traditional sales organizations do.
The bottom line? In SaaS, the initial sale is just the beginning of the revenue journey.
What is the SaaS sales funnel?
The SaaS sales funnel maps the journey prospects take from discovering your product to becoming loyal customers. This framework helps sales teams organize their approach at the different SaaS sales stages.
Unlike traditional funnels that end at purchase, the SaaS funnel extends to include retention and expansion—reflecting the subscription-based business model.
Modern SaaS funnels blend marketing and sales activities seamlessly to create a cohesive experience as prospects move through their buying journey.
Your funnel metrics reveal where prospects drop off and which stages need optimization. This data-driven approach is crucial for efficiently scaling your B2B SaaS sales strategy.
SaaS sales funnel stages
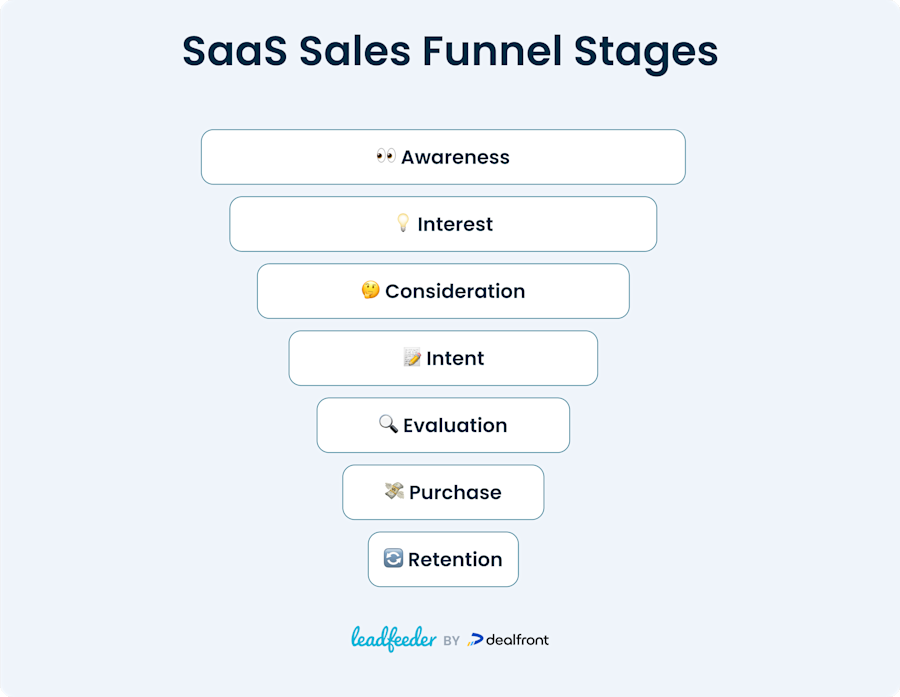
1. Awareness
Potential customers recognize a problem and begin searching for solutions. Your marketing team drives awareness through content, social media, and advertising targeted at people experiencing the challenges you solve.
2. Interest
Prospects discover your solution and begin evaluating it against their needs. They might subscribe to your newsletter, download resources, or explore your website. Focus on education rather than selling at this stage.
3. Consideration
Prospects actively compare options, weighing features and pricing against their requirements. Your sales team makes contact through discovery calls or demos to understand their situation and position your solution as the ideal fit.
4. Intent
Prospects signal they're leaning toward your solution by requesting quotes, starting trials, or asking implementation questions. Conversations should focus on specific use cases, return on investment (ROI), and addressing technical concerns.
5. Evaluation
Prospects conduct final due diligence, often requesting references, security documentation, and customization options. This stage typically involves multiple stakeholders with different priorities.
6. Purchase
The prospect becomes a customer through contract signing. This transition requires smooth handoffs between B2B SaaS sales and customer success teams, clear implementation expectations, and transparent communication.
7. Retention and advocacy
Customer success teams ensure ongoing value through regular check-ins, usage analysis, and proactive support. Successful customers become advocates, creating a cycle that feeds new prospects into your SaaS sales funnel.
SaaS sales process and strategy
An effective SaaS sales process provides a structured framework your team can follow to consistently move prospects toward purchase decisions. Getting this process right saves time, improves conversion rates, and creates a better experience for your prospects.
Let's break down the five key stages of a successful SaaS sales strategy:

1) Lead generation
Lead generation focuses on attracting potential customers who might benefit from your solution. Your marketing team typically handles much of this work through content marketing, digital advertising, and SEO efforts.
Effective strategies for SaaS sales and marketing include:
Gated content offers (whitepapers, templates, tools)
Webinars addressing industry pain points
Free trials or "freemium" versions of your product
Strategic partnerships with complementary services
2) Outbound Prospecting
Outbound prospecting involves proactively reaching out to potential customers who fit your solution profile. Sales development representatives (SDRs) typically own this process, using research-based approaches to connect with decision-makers.
Modern outbound prospecting requires:
Thorough research of target companies
Personalized messaging addressing specific pain points
Multi-channel outreach (email, phone, social)
Persistence without being pushy
3) Sales qualification
Qualification separates prospects with genuine potential from those unlikely to convert. This is a critical step in any enterprise SaaS sales process and will save your team countless hours.
Effective qualification frameworks like BANT (Budget, Authority, Need, Timeline) or MEDDIC (Metrics, Economic buyer, Decision criteria, Decision process, Identify pain, Champion) help structure these conversations. Ask thoughtful questions about:
Current challenges and their business impact
Decision-making process and stakeholders involved
Budget availability and purchasing timeline
Technical requirements and integration needs
Document these insights carefully—they'll guide your approach throughout the remaining B2B SaaS sales process.
Leadfeeder for sales can streamline this process for SaaS sales teams by providing dozens of powerful, customizable filters. Integrate Leadfeeder with your CRM and automate the filling of your pipeline with high-value prospects sorted by company size, location, how they found your site, and so much more.
4) Sales demos
Demos should showcase how your solution solves the prospect's specific problems. But avoid generic presentations. Instead, tailor each demo to address the unique challenges you uncovered during qualification.
Key steps you can take to achieve effective SaaS demos include:
Starting with the most relevant features for their use case
Showing, not telling—use real-world scenarios they'll encounter
Addressing potential objections proactively
Including clear next steps at the conclusion
Remember that your goal isn't to showcase every feature. Focus on demonstrating value and ROI for their specific situation.
5) Closing
The closing stage converts qualified opportunities into paying customers. This involves finalizing agreements, addressing any remaining concerns, and setting expectations for implementation and onboarding.
Effective closing techniques include:
Summarizing the agreed-upon value proposition
Creating a sense of urgency without pressure tactics
Proactively addressing procurement processes
Making the contract and payment process frictionless
Once closed, ensure a smooth handoff from your B2B SaaS sales team to your customer success team to maintain momentum and deliver on promised value.
SaaS sales activities
Your daily sales activities determine your results. While every organization has unique approaches, three core activities typically drive SaaS sales success.
1) Cold calling
Despite predictions of its demise, strategic cold calling remains effective for SaaS sales. Today's approach is more research-based and consultative than the aggressive scripts of the past.
Effective cold calls start with thorough preparation. Research the company's recent news, understand its industry challenges, and identify specific ways your solution might help. Your goal isn't selling on the first call—it's starting a conversation.
Keep calls brief and focused on qualifying interest and scheduling a more in-depth discussion. Track your call metrics to continuously refine your approach and timing.
2) Outbound email
Email outreach allows you to reach more prospects with personalized messages. The key is standing out in crowded inboxes with relevant, value-added content.
Best practices for outbound SaaS sales emails include having:
Personalized subject lines with specific references
Brief, scannable content (three to five sentences maximum for each paragraph)
Clear value proposition tailored to their role
One specific call-to-action
Sequence your emails thoughtfully rather than sending one-off messages. A strategic cadence with varied messaging increases your chances of connecting at the right moment.
3) Social selling
Social selling involves using social platforms (especially LinkedIn) to connect with prospects, share valuable insights, and build relationships. This approach complements traditional outreach by establishing credibility and trust.
Effective social selling tactics include:
Engaging with prospect's content through comments
Sharing relevant industry insights and articles
Connecting after meaningful interactions at events
Using direct messages for personalized outreach
When done right, social selling creates warm introductions that bypass gatekeepers and position you as a trusted advisor rather than just another vendor.
SaaS sales cycle
Understanding your sales cycle helps you set realistic expectations and allocate resources effectively. Several factors influence how quickly deals move through your pipeline:
Product complexity: More complex solutions typically take longer to sell.
Price point: Higher costs generally extend decision timelines.
Number of stakeholders: More decision-makers means longer cycles.
Implementation requirements: Complex integrations extend the process.
Customer size: Enterprise deals move slower than SMB transactions.
Track your cycle data by segment to identify opportunities for streamlining without rushing necessary relationship-building conversations.
Length of SaaS sales cycles
The length of SaaS sales cycles can vary dramatically based on several key factors:
Price point is a primary determinant:
Products under $5,000: 30-45 days
Mid-market ($5,000-$50,000): one to three months
Enterprise ($50,000+): three to six months plus
Product customization options:
More complex configurations require additional demos and technical discussions, often extending the cycle by weeks or months.
Company size impacts stakeholder involvement:
SMBs: one to two decision-makers (faster cycles)
Mid-market: three to five decision-makers
Enterprise: six to ten or more decision-makers (slowest cycles)
Remember to factor marketing activities into your timeline calculations. Free trials, onboarding processes, and implementation planning all contribute to the overall cycle length.
Which SaaS sales model should you use?
Your sales model should match your product complexity, price point, and who you're selling to. Three primary approaches dominate the SaaS market:
1) Self-service model
Perfect for straightforward, affordable solutions under $1,000 annually. Customers purchase directly online with minimal sales interaction. Your website and product do most of the selling, while marketing drives acquisition.
2) Transactional sales model
This middle-ground approach works well for mid-market solutions ($1,000-$15,000). Sales reps guide prospects through a defined process with consultative discussions, typically closing within one to three months.
3) Enterprise sales model
Complex solutions over $15,000 need a high-touch, relationship-driven approach. Multiple stakeholders, customized demos, and thorough security reviews extend sales cycles to six months or more.
How to build a SaaS sales strategy in six steps
Building an SaaS sales operation doesn't have to be complicated. These six practical steps essentially provide an SaaS sales process template you can customize to your specific solution.
Step 1: Pick a sales model
Your sales model shapes everything, from how you hire to how you compensate your team. Choose based on what makes sense for your product and target customers.
Many successful SaaS companies run multiple models simultaneously. You might offer self-service for small businesses while maintaining an enterprise team for larger clients.
Step 2: Spot your target audience
A clear ideal customer profile (ICP) prevents wasted effort and accelerates growth. Dig beyond basic demographics to understand what makes your best customers tick.
Look for patterns in your current customer base:
Which industries see the biggest ROI from your solution?
Which company sizes have the highest retention rates?
Which roles typically champion your product internally?
Create detailed buyer personas capturing both company characteristics and individual motivations. What keeps your prospects awake at night? What would make them look like heroes to their bosses?
Remember—narrowing your focus actually improves results. You can't be everything to everyone.
Step 3: Craft a value proposition
A compelling value proposition answers one simple question: "Why should I buy from you instead of doing nothing or choosing a competitor?"
Make it specific, meaningful, and tied to outcomes your prospects actually care about.
Strong value propositions include:
The problem you solve (pain point)
How you solve it (unique approach)
Concrete results customers can expect (value)
Ditch vague claims like "innovative platform" or "world-class solution." Instead, focus on specific impacts like "reduce customer response times by 40% while handling twice the volume."
Step 4: Qualify prospects
Every lead deserves attention—but not equal amounts of it. Create a systematic qualification process to identify which prospects deserve deeper investment from your sales team.
Consider these qualification factors:
Factor |
Key Question |
Why It Matters |
Fit |
Does the prospect match your ICP? |
Prevents wasted effort |
Need |
Do you solve the problem they have? |
Determines relevance |
Budget |
Can they afford your solution? |
Ensures viability |
Authority |
Can your contact influence the decision? |
Prevents dead ends |
Timeline |
Does the problem need solving urgently? |
Indicates likelihood to act |
Create a simple scoring system that helps prioritize opportunities. This ensures your best prospects get the attention they deserve while lower-quality leads don't consume disproportionate resources.
Step 5: Create a selling strategy
Your selling strategy maps out how you'll move qualified prospects through your pipeline. This includes outreach methods, messaging approaches, and techniques for handling common objections.
Resources that can be used to support each stage include:
Email templates and call frameworks (not rigid scripts)
Customer stories showing concrete results
ROI calculators tailored to different industries
Competitor comparison guides
Implementation roadmaps
Step 6: Decide goals and track performance
Clear, measurable objectives create focus and accountability. Identify key SaaS sales metrics and review them regularly.
Consider tracking:
Win rate (opportunities that close)
Average deal size (typical contract value)
Sales cycle length (time from first contact to close)
Customer acquisition cost (total spend per new customer)
Look beyond the numbers to understand the stories they tell. Why are certain reps outperforming others? What do your fastest-closing deals have in common?
The goal isn't data collection for its own sake. It's using insights to constantly refine your approach and drive sustainable growth.
How to track your SaaS sales metrics
Tracking the right metrics helps you understand what's working and where you need to improve. Different roles need different measurements to drive the behaviors that matter most.
SDR KPIs
Sales Development Representatives (SDRs) need metrics that measure both activity and outcomes:
Productivity metrics:
Emails sent per day/week
Direct dials completed
LinkedIn connection requests and InMails sent
Response rates across channels
Success metrics:
Meetings booked and held
Sales qualified opportunities (SQOs) generated
Conversion rate from lead to opportunity
Average time to qualification
BDM KPIs
Business Development Managers (BDMs) should focus on metrics that track closing effectiveness:
Personal performance:
Average deal size
Win rate (opportunities to close deals)
Sales cycle length
Revenue metrics:
Monthly recurring revenue (MRR) booked
Percentage of target achieved
Expansion revenue from existing accounts
Pipeline health:
Number of active opportunities
Demo-to-contract conversion rate
Reasons for lost opportunities
Inbound vs outbound
Comparing these channels helps optimize your resource allocation:
Conversion metrics:
Lead-to-opportunity rate by source
Opportunity-to-close rate by source
Average deal size for each channel
Revenue contribution:
Total revenue from inbound vs outbound
Customer acquisition cost by channel
Lifetime value by acquisition source
Seven best SaaS sales methodologies for increased revenue
Different approaches work better for different SaaS products and customer segments. The best SaaS sales methodology aligns with your specific selling environment and buyer journey.
1) SPIN selling
SPIN (Situation, Problem, Implication, Need-payoff) focuses on asking strategic questions that help prospects recognize their own needs. Successful SaaS sales examples show that this consultative approach works particularly well for complex solutions.
Key strength: Helps customers self-discover the value of your solution rather than being "sold to."
2) MEDDIC
MEDDIC (Metrics, Economic Buyer, Decision criteria, Decision process, Identify pain, Champion) provides a structured qualification framework that's ideal for enterprise SaaS sales. It helps identify whether opportunities are worth pursuing and what's needed to win them.
Key strength: Improves forecast accuracy and focuses resources on winnable deals.
3) Challenger sale
The Challenger approach centers on pushing prospects' thinking with new insights about their business. Instead of relationship building, it focuses on constructive tension and reframing problems in ways prospects hadn't considered.
Key strength: Differentiates your solution in crowded SaaS categories where features often seem similar.
4) Solution selling
This methodology concentrates on understanding customer pain points and positioning your SaaS product as the specific solution. It involves deep discovery to uncover both obvious and hidden challenges.
Key strength: Creates strong alignment between customer needs and your product capabilities.
5) Sandler methodology
The Sandler methodology emphasizes mutual qualification, where both seller and buyer assess fit throughout the process. It balances assertiveness with respect for the prospect's time by addressing mismatches early.
Key strength: Creates more honest sales conversations and reduces time wasted on poor-fit opportunities.
6) SNAP selling
SNAP (Simple, iNvaluable, Aligned, Priority) focuses on making buying decisions easier for overwhelmed prospects. It acknowledges today's busy decision-makers by simplifying complex SaaS solutions.
Key strength: Overcomes decision paralysis in prospects facing too many options.
7) Gap selling
Gap selling identifies the difference between a customer's current state and their desired future state. The larger this gap is, the more compelling the reason to purchase your solution.
Key strength: Creates urgency by quantifying the cost of not addressing problems with your SaaS solution.
Challenges of SaaS sales
The SaaS sales environment comes with unique obstacles that require specific strategies to overcome. Understanding these challenges helps you develop effective approaches to address them.
1) Long and complex sales cycles
Multiple decision-makers and lengthy approval processes can significantly delay closings. Combat this by creating clear buying paths with defined milestones for each stakeholder. Setting proper expectations about the timeline from the start also helps maintain momentum.
2) Increasing market competition
As more players enter the SaaS space, differentiation becomes crucial. Focus conversations on your unique value proposition and specific customer outcomes rather than getting trapped in feature-comparison discussions that commoditize your offering.
3) Security and compliance concerns
Enterprise prospects often have rigorous security requirements that slow down deals. Prepare standardized documentation, involve technical specialists early, and consider obtaining relevant certifications to accelerate this process.
4) Evolving product features
Rapid development cycles make it challenging for SaaS sales teams to stay current on capabilities. Implement regular product training and create simplified feature guides organized by use case rather than technical specifications.
5) Customer expectations for immediate value
The pressure for faster time-to-value grows stronger each year. Set realistic implementation timelines and create roadmaps that highlight early wins before your product is fully deployed.
6) Subscription fatigue
As businesses juggle more recurring expenses, adding another subscription faces increasing scrutiny. Emphasize ROI calculations and offer flexible contract terms that align with the customer's budget cycles.
7) Proving ROI before purchase
The benefits of SaaS often emerge over time rather than immediately after implementation. Use case studies, customer testimonials, and limited free trials that demonstrate value quickly to overcome this hurdle.
Five tips for successful SaaS selling
Want to outperform the competition? These five practical approaches will strengthen your SaaS sales efforts:
1) Lead with value, not features
Focus conversations on business outcomes rather than technical capabilities. Customers don't buy software—they buy solutions to problems and ways to achieve goals. Connect every feature to a tangible benefit for the specific customer you're talking to.
2) Embrace product-led growth alongside sales
Create opportunities for prospects to experience your product before formal sales conversations. Freemium models, interactive demos, or free trials build familiarity and conviction. Your sales team can then focus on expanding usage rather than introducing basic concepts.
3) Build a customer-centric sales process
Design your sales approach around how customers actually buy, not how you prefer to sell. Map their journey, identify friction points, and streamline steps that slow down decisions. Adjust your process based on feedback and changing market conditions.
4) Invest in ongoing sales education
SaaS trends evolve incredibly fast. Set aside dedicated time for your team to learn about industry trends, competitive offerings, and emerging customer needs. Create systems for sharing knowledge between customer-facing teams.
5) Align sales incentives with customer success
Structure compensation to reward not just closed deals but successful implementations and renewals. This encourages proper qualification and setting realistic expectations. When customers succeed with your product, everyone wins.
Master SaaS sales and drive scalable growth
Ready to take your SaaS sales to the next level? The strategies and frameworks in this guide give you the tools to build a sales operation that delivers consistent results while adapting to emerging SaaS trends.
Your success hinges on three things:
Truly understanding your buyers' challenges
Delivering value in every interaction
Staying laser-focused on customer outcomes
The difference between good and great? It's all in the execution.
Curious how to uncover hidden opportunities already in your funnel? Leadfeeder reveals which companies browse your site without filling out forms. Talk about a competitive edge! Your team can reach out to prospects already showing interest—often slashing those sales cycles dramatically.
That's sales intelligence that actually moves the needle. Sign up for a free trial to experience it for yourself today.
FAQs about SaaS sales
What is the 3 3 2 2 2 rule of SaaS?
The 3 3 2 2 2 rule serves as a quick benchmark for healthy SaaS businesses. It suggests aiming for three times the customer acquisition cost (CAC) payback, 3% net monthly revenue churn, two times the year-over-year growth, two or fewer years of negative cash flow, and two hours of daily CEO involvement in sales. These targets help balance growth with sustainability.
How do you build an SaaS sales team?
Start by defining clear roles aligned with your sales model. Typically, begin with a Sales Development Representative (SDR) for qualification and an Account Executive (AE) for closing. Set clear expectations, create repeatable processes, and implement proper onboarding. As you scale, add specialized roles like solution engineers and account managers.
Why is it a good idea to start a career in SaaS sales?
SaaS sales offers exceptional income potential, clear career progression, and transferable skills. The recurring revenue model creates predictable commission structures, while the tech industry's growth provides long-term stability.
Now that you're here
Leadfeeder is a tool that shows you companies that visit your website. Leadfeeder generates new leads, offers insight on your customers and can help you increase your marketing ROI.
If you liked this blog post, you'll probably love Leadfeeder, too.
Sign up




